Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
沖田 将一朗; 後藤 実
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The recently released JENDL-5 and ENDF/B-VIII.0 have adopted porosity-dependent thermal neutron scattering law (TSL) data for reactor graphite, and they improve neutronic calculation accuracy of criticality for graphite-moderated cores. Currently, we can only handle neutronic calculations for three graphite porosities of 0%, 10%, and 30%. The uncertainties associated with the difference between the porosity of actual reactor graphite ( 20%) and the porosity remains. Toward the future update of JENDL-5, we are planning to preparing new TSL data of reactor graphite. As a first step, it is essential to evalute phonon density state distribution of reactor graphite. In this study, in order to evalute it, molecular dynamic (MD) analysis is performed for three MD models: ideal crystalline graphite (Ideal model), 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore (Monoatomic random model), and 20%-porous reactor graphite with atomic cluster random pore (Cluster random model). The ideal crystalline graphite is modeled without any pores for reference. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore is modeled by randomly removing atoms from the ideal crystalline graphite. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with cluster random pore is modeled by randomly removing atomic clusters of approximately 2 nm in diameter from the ideal crystalline graphite. Their interatomic interactions are on the basis of Reactive Empirical Bond Order (REBO) potential. Velocity autocorrelation functions and phonon density of states distributions are calculated for these models. For validation, specific heat for each model is evaluated, and they are compred with experimental values.
20%) and the porosity remains. Toward the future update of JENDL-5, we are planning to preparing new TSL data of reactor graphite. As a first step, it is essential to evalute phonon density state distribution of reactor graphite. In this study, in order to evalute it, molecular dynamic (MD) analysis is performed for three MD models: ideal crystalline graphite (Ideal model), 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore (Monoatomic random model), and 20%-porous reactor graphite with atomic cluster random pore (Cluster random model). The ideal crystalline graphite is modeled without any pores for reference. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with monoatomic random pore is modeled by randomly removing atoms from the ideal crystalline graphite. The 20%-porous reactor graphite with cluster random pore is modeled by randomly removing atomic clusters of approximately 2 nm in diameter from the ideal crystalline graphite. Their interatomic interactions are on the basis of Reactive Empirical Bond Order (REBO) potential. Velocity autocorrelation functions and phonon density of states distributions are calculated for these models. For validation, specific heat for each model is evaluated, and they are compred with experimental values.
市原 晃
JAEA-Review 2019-046, 36 Pages, 2020/03
JENDL-4.0の改定に向けて、液体に対する熱中性子散乱断面積の計算法に関する文献調査を実施した。本報告書は、分子動力学シミュレーションを利用した熱中性子散乱断面積の計算法を要約したものである。断面積は「散乱則」と呼ばれる関数を使って表され、軽水や重水に対しては断面積の代わりに散乱則に関するデータが核データベース上で与えられている。本調査で散乱則の計算法を確認した。散乱則は中間散乱関数と時空間相関関数の両者から導くことができる。得られる散乱則の特徴について言及した。熱中性子のターゲットである液体の分子動力学シミュレーションを利用して散乱則が計算できることを示した。
Cullen, D. E.*; Blomquist, R. N.*; Dean, C.*; Heinrichs, D.*; Kalugin, M. A.*; Lee, M.*; Lee, Y. K.*; MacFarlane, R.*; 長家 康展; Trkov, A.*
UCRL-TR-203892, p.1 - 40, 2004/04
熱中性子炉体系において熱中性子散乱は非常に重要であり、熱中性子散乱を正確に取り扱わなければならない。モンテカルロコードで熱中性子散乱を取り扱う場合、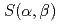 データやFree Gasモデルに基づいて散乱解析が行われるが、その取り扱いはコードごとに異なっているのが普通である。また、用いられる熱中性子散乱データが異なれば結果が異なってくる。本研究では、さまざまなモンテカルロコードパッケージ(コードと核データ)を用いて、熱中性子散乱の影響を受けやすい体系において実効増倍率などの積分パラメータをどの程度正確に求めることができるか調べるためのベンチマークを実施した。ベンチマーク計算では、熱中性子散乱の効果が強調されるような非常に簡単なピンセル体系について
データやFree Gasモデルに基づいて散乱解析が行われるが、その取り扱いはコードごとに異なっているのが普通である。また、用いられる熱中性子散乱データが異なれば結果が異なってくる。本研究では、さまざまなモンテカルロコードパッケージ(コードと核データ)を用いて、熱中性子散乱の影響を受けやすい体系において実効増倍率などの積分パラメータをどの程度正確に求めることができるか調べるためのベンチマークを実施した。ベンチマーク計算では、熱中性子散乱の効果が強調されるような非常に簡単なピンセル体系について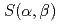 データを用いる場合とFree Gasモデルの場合の実効増倍率を計算し、比較した。熱中性子散乱効果は体系依存性が強く、このベンチマーク体系では5%から12%もあることがわかった。コード間の比較では
データを用いる場合とFree Gasモデルの場合の実効増倍率を計算し、比較した。熱中性子散乱効果は体系依存性が強く、このベンチマーク体系では5%から12%もあることがわかった。コード間の比較では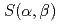 により熱中性子散乱を考慮した場合は実効増倍率で
により熱中性子散乱を考慮した場合は実効増倍率で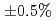 、Free Gasモデルの場合で
、Free Gasモデルの場合で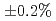 のばらつきがあることがわかった。
のばらつきがあることがわかった。
中原 康明
JAERI-M 5245, 65 Pages, 1973/04
炉物理の立場から見た中性子減速材としての黒鉛の物理的性質と熱中性子散乱特性に関する理論的及び実験的研究の現状や筆者自身の計算の結果のまとめを行った。黒鉛の構造と特徴、黒鉛結晶中の原子の格子振動の解析法や振動数分布の理論値と実験値、熱中性子散乱断面積の計算法、計算コード、データ・ライブラリー、散乱断面積の計算値と実験値等についての解説及び議論を行った。